Power factor:
In power system, three quantities
are most important;
1)
Voltage
2)
Current
3)
Frequency
Power quality is an important concern in the power system because it affects the voltage,
current, and frequency. The power factor
is an important aspect for improving power quality of supply. A load with low
power factor has good efficiency and it can save a considerable amount of cost. For, this reason, majority of the
utility companies demand in the reduction
of reactive power. If reactive power demand decrease, the power factor will improve.
1)
Apparent power
2)
Active power
3)
Reactive power
1) Apparent power:
The
apparent power is denoted as ‘S’. It is the product of the RMS voltage and current. Volt-amperes or VA is
unit of the apparent power.
S = V x I for single phase apparent power
S = 1.73 V x I for three phase apparent power
Where V is phase
voltage and I is line current
2) Active Power:
The active power
is also known as true power or real power. This power is a useful power for the load. The unit of the
active power is WATT (W) and it is denoted as P. WATT is a very small unit, so
power is measured in kW or MW. The active power is carried out in the power
system by the part of the current. This current is always in phase with the supply
voltage. The real work cannot be done when the current is out of phase with the
supply voltage.
3) Reactive power:
The reactive power is a part of an apparent
power which is out phase with the real power. This is happening in the power
system by reactive elements like
inductors and capacitors. This power does not use
for the load. The reactive power is also known as the imaginary power. The unit
of the reactive power is volt-ampere-reactive (VAR).
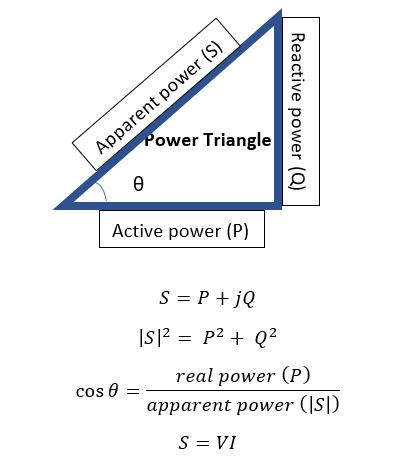
Power factor:
The
power factor is the ratio of active power (true power) to the power supplied by
the power system (apparent power).
POWER FACTOR = REAL
POWER / APPARENT POWER
PF
= P/S
In power triangle, θ is the angle between
current and voltage. Power factor is also defined as the cosine angle between
the phase voltage and the line current.
PF
= cos θ
Power factor is a
dimensionless quantity. The range of
power factor is between -1 to 1. In an ideal
power system, the power factor is unity
(1), means that there is only real power is available. There is absent of
reactive power. But in the actual power
system, we can not ignore the reactive power and it always is present in the power system. So, in the actual power system, the power system can not unity, but for good
quality of supply, we try to maintain power factor near to the unity.
In the power system, we use FACTS devices to improve
the power factor.

0 comments:
Post a Comment